Geospatial assessment of land use/land cover change and land surface temperature dynamics using multi-index analysis and CA-Markov modeling from 1990-2022 in Lahore, Pakistan
Keywords:
LST, Urbanization, LULC, Urban heat island, CA MarkovAbstract
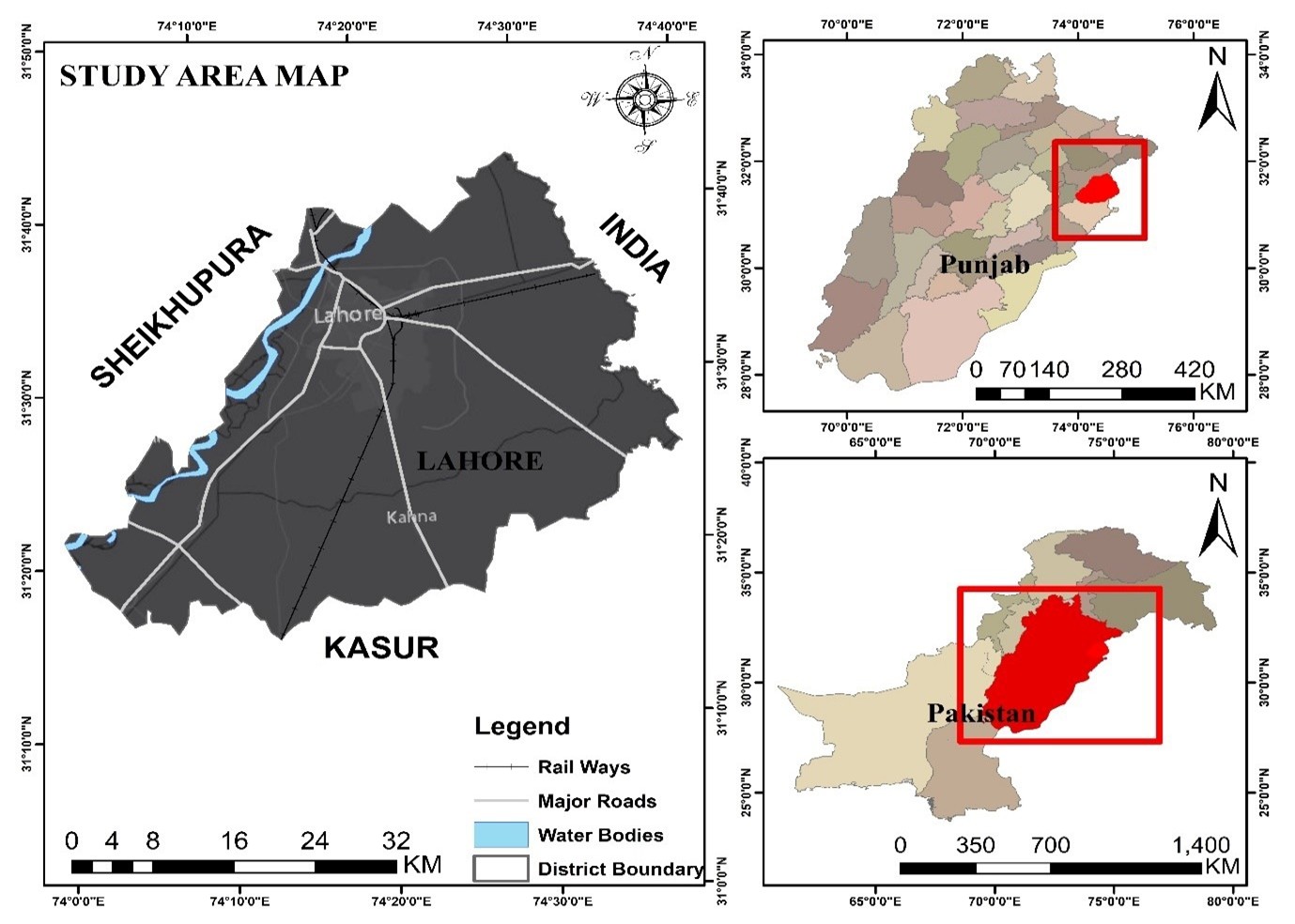
The rapid urbanization has notably changed land use/ land cover (LULC) patterns of South Asian megacities, which intensifies the temperature of the land surface (LST) and urban heat islands. The consequences of urbanization on the climate and environment are critical for the natural resource management. This study examines long-term LULC dynamics and its effect on LST in Lahore, Pakistan, between 1990 and 2022 using multi-temporal Landsat data, various spectral indices and CA-Markov model to further predict future changes. Findings indicate that the vegetation cover decreased by about 71% in 1990 to 45.53% in 2022, with the settlement areas increasing by 13.54 to 36.78%. The overall accuracy of images ranged from 89 to 90%. Correspondingly, mean LST increased from 30 ºC up to more than 50 ºC. The correlation analysis showed that NDVI had strong negative correlation with LST but NDBI, NDBaI and NDWI and Urban Index had strong positive correlation with LST, demonstrating the importance of impervious and barren areas in intensifying heat. According to CA-Markov projections, settlement areas could increase more than 45% of the total area by 2050 with a further decrease in vegetation to almost 37%. These findings underline the importance of urban planning and sustainable land management that is climate sensitive so that the future thermal stress of rapidly growing cities can be reduced. The research also presents the understanding of LULC dynamics and promoting dialogs about the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)-climate action and building resilient cities and communities.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 SciNex Journal of Advanced Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




 SCINEX PUBLISHERS
SCINEX PUBLISHERS